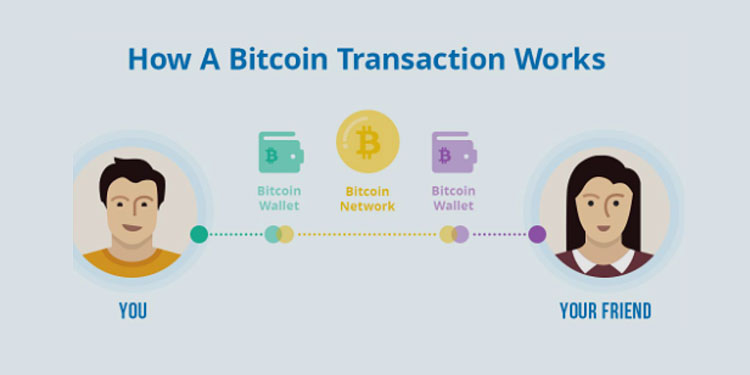
Bitcoin is a form of digital currency that allows people to exchange money without the need for a central authority. Bitcoin transactions work by transferring value between users, with no bank or clearinghouse in between.
As there is no intermediary between the transactions, the transaction is completely anonymous. You can buy anything you want from a coffee to a Bitcoin VPS anonymously with bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency available.
Bitcoin transactions are verified by a network of computers called miners that use software to solve complex mathematical equations. These equations verify each transaction and record it in a public ledger, which is known as the blockchain. It’s important to note that bitcoin transactions are irreversible and cannot be canceled as well.
Bitcoin’s value can fluctuate depending on how much people trust it – but at this point in time, bitcoin has been gaining momentum and acceptance.
What is a Transaction?
A transaction is an exchange of value between two parties. A transaction can be a purchase, sale, barter, gift, or donation. It can also include the transfer of goods and services from one person or company to another.
Transactions can be categorized by the type of good or service being exchanged. For example, we might say that a car sale is a purchase transaction, and a wedding ceremony is a donation transaction.
Transactions can also be classified into two types: bilateral and unilateral. A bilateral transaction is one in which both parties in the exchange agree on all terms and conditions. A unilateral transaction occurs when one party agrees to all of the terms and conditions but there is no agreement between the two parties involved in the exchange.
After all, in simple terms, we can say that a transaction is giving “something for something” in return.
How do transactions work in the crypto world?
The crypto world is a new and exciting place for many people. In the past, people had to rely on banks or other traditional financial institutions to handle their transactions. However, with the advent of cryptocurrencies, people can now do transactions without having to go through those channels. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin are used as a medium of exchange or store of value because they can be easily traded with fiat currencies like USD or EUR.
Transactions in the crypto world are very different from what we are used to when transacting in fiat currencies. The main difference is that there is no central authority or bank involved in these transactions – those are replaced by blockchains and smart contracts. Transactions are also not limited by time or location – they can be done at any time and anywhere in the world where there is
Cryptocurrency exchanges are where you can buy and sell cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin. The exchange takes your fiat currency (like USD or EUR) and converts it into cryptocurrency. Once you have your cryptocurrency you can then transfer it to a wallet or exchange it for other cryptocurrencies or fiat currency again on an exchange.
Crypto wallets store your cryptocurrency securely so that it cannot be stolen by hackers or government officials if they get access to them. And lastly, exchanges allow you to trade one cryptocurrency for another or to send cryptocurrency to another person.
How are Bitcoin transactions done?
The first step in using Bitcoin is setting up an account with a service like Coinbase or BitPay. After you have your account set up, you can buy and sell Bitcoins on these exchanges. You can also use your account to send or receive payments from other users. Once you have bought Bitcoins, you can send them to someone else who will then transfer them into their wallet for future use.
Bitcoin transactions are done by sending a transaction request to the Bitcoin network. This request contains information about who wants to send bitcoin and where they want it sent. The transaction is then broadcasted on the network, and verified by all nodes on the network before being added to the blockchain.
The transactions are recorded in blocks that are added chronologically, with each block containing a cryptographic hash of its predecessor so as to link them in a chain. This link makes it impossible for someone to spend any bitcoin more than once without consent from every other node on the network.
These cryptographic hashes are decoded by the miners on the network using their computer power, and once verified they are added to the blockchain and the transaction will be immediately processed and finalized.
How much is Bitcoin’s transaction fee?
Bitcoin’s transaction fee is the amount paid to the miners who maintain the decentralized network of bitcoin transactions. The fees are collected by mining pools and sent to their miners, which in turn, distribute these fees among themselves according to how much work they contributed towards solving a block of transactions.
The transaction fee is very low at present because most people are still using Bitcoin for small purchases and not for large payments.
The transaction fee is the amount of bitcoin that you have to pay for every single transaction. In 2010, a minimum transaction fee of 0.01BTC was imposed as a source code rule. After some time, this rule was deposed as the amount of transaction volume increased.
You can find the dynamics of bitcoin transaction rates here.
The fees are used by miners to incentivize them to process your transaction and add it to the blockchain in a timely manner. If your transaction doesn’t get processed in time or gets rejected by miners, then it will be considered as an orphaned block and won’t be added into the blockchain at all.
Miners are essential for the bitcoin network to preserve. As bitcoin price increases in the market, the dollar value of the transaction fee changes and therefore, transaction fees are increased from time to time considering the transaction volume of the network and the computer power needed to decode a hash of a transaction.